#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node{
int arr[10][10];
int i,j;
int h;
};
int a[10][10];
struct node* head = NULL;
struct node* q[200];
int check(int n);
void insert(int n);
int r=0,c=0,gotit;
void operations(int k,int m,int n);
void display(int n);
main()
{
int n=3;
insert(n);
display(n);
}
void insert(int n)
{
int i,j;
struct node *temp;
temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
printf("Enter 8 puzzle matrix");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&temp->arr[i][j]);
}
}
printf("Enter 8 puzzle matrix goal state");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(temp->arr[i][j]==0)
{
temp->i = i;
temp->j = j;
}
}
}
int count=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(temp->arr[i][j]!=a[i][j] && a[i][j]!=0)
{
count++;
}
}
}
temp->h = count;
int k,m;
q[r] = temp;
while(1)
{
k = q[r]->i;
m = q[r]->j;
if(++k<n && m<n && (k>=0 && m>=0))
{
operations(k,m,n);
}
k = q[r]->i;
m = q[r]->j;
if(--k<n && m<n&& (k>=0 && m>=0))
{
operations(k,m,n);
}
k = q[r]->i;
m = q[r]->j;
if(k<n && --m<n&& (k>=0 && m>=0))
{
operations(k,m,n);
}
k = q[r]->i;
m = q[r]->j;
if(k<n && ++m<n&& (k>=0 && m>=0))
{
operations(k,m,n);
}
r++;
struct node* swap;
// This for loop is sorting acc to h(n)
for(i=r;i<=c;i++)
{
for(j=r;j<=c-1;j++)
{
if(q[j]->h>q[j+1]->h)
{
swap = q[j];
q[j] = q[j+1];
q[j+1] = swap;
}
}
}
c=r;
if(check(n)==-4)
{
break;
}
}
}
//
void operations(int k,int m,int n)
{
int o,p,count=0;
struct node* t;
t = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
t->arr[i][j] = q[r]->arr[i][j];
}
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(t->arr[i][j]==0)
{
o = i;
p=j;
}
}
}
int swap = t->arr[o][p];
t->arr[o][p] = t->arr[k][m];
t->arr[k][m] = swap;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(t->arr[i][j]==0)
{
t->i = i;
t->j = j;
}
}
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(t->arr[i][j]!=a[i][j] && a[i][j]!=0)
{
count++;
}
}
}
t->h = count;
c++;
q[c] = t;
}
int check(int n)
{
int i,j,k,i1,i3,c1=0,c2,g2=0;
int count=0;
// here it is removing the node if duplicate matrix is present
for(i=0;i<c;i++)
{
for(i3=i+1;i3<c;i3++)
{
count = 0 ;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
for(k=0;k<n;k++)
{
if(q[i]->arr[j][k]==q[i3]->arr[j][k])
{
count++;
}
}
}
if(count==9)
{
for(i1=i3;i1<c;i1++)
{
q[i1] = q[i1+1];
}
c--;
count = 0;
}
count = 0;
}
}
// here it is checking whether the goal state is finding or not
c2=0;
for(i1=0;i1<c;i1++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
for(k=0;k<n;k++)
{
if(q[i1]->arr[j][k]==a[j][k])
{
c2++;
}
}
}
if(c2==9)
{
gotit = i1;
g2 = -4;
break;
}
else{
c2=0;
}
}
return g2;
}
// Displaying path
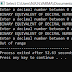
void display(int n)
{
int i,j,k;
for(i=0;i<r;i++)
{
printf("\n");
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
for(k=0;k<n;k++)
{
printf("%d\t",q[i]->arr[j][k]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node{
int arr[10][10];
int i,j;
int h;
};
int a[10][10];
struct node* head = NULL;
struct node* q[200];
int check(int n);
void insert(int n);
int r=0,c=0,gotit;
void operations(int k,int m,int n);
void display(int n);
main()
{
int n=3;
insert(n);
display(n);
}
void insert(int n)
{
int i,j;
struct node *temp;
temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
printf("Enter 8 puzzle matrix");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&temp->arr[i][j]);
}
}
printf("Enter 8 puzzle matrix goal state");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(temp->arr[i][j]==0)
{
temp->i = i;
temp->j = j;
}
}
}
int count=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(temp->arr[i][j]!=a[i][j] && a[i][j]!=0)
{
count++;
}
}
}
temp->h = count;
int k,m;
q[r] = temp;
while(1)
{
k = q[r]->i;
m = q[r]->j;
if(++k<n && m<n && (k>=0 && m>=0))
{
operations(k,m,n);
}
k = q[r]->i;
m = q[r]->j;
if(--k<n && m<n&& (k>=0 && m>=0))
{
operations(k,m,n);
}
k = q[r]->i;
m = q[r]->j;
if(k<n && --m<n&& (k>=0 && m>=0))
{
operations(k,m,n);
}
k = q[r]->i;
m = q[r]->j;
if(k<n && ++m<n&& (k>=0 && m>=0))
{
operations(k,m,n);
}
r++;
struct node* swap;
// This for loop is sorting acc to h(n)
for(i=r;i<=c;i++)
{
for(j=r;j<=c-1;j++)
{
if(q[j]->h>q[j+1]->h)
{
swap = q[j];
q[j] = q[j+1];
q[j+1] = swap;
}
}
}
c=r;
if(check(n)==-4)
{
break;
}
}
}
//
void operations(int k,int m,int n)
{
int o,p,count=0;
struct node* t;
t = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
t->arr[i][j] = q[r]->arr[i][j];
}
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(t->arr[i][j]==0)
{
o = i;
p=j;
}
}
}
int swap = t->arr[o][p];
t->arr[o][p] = t->arr[k][m];
t->arr[k][m] = swap;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(t->arr[i][j]==0)
{
t->i = i;
t->j = j;
}
}
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(t->arr[i][j]!=a[i][j] && a[i][j]!=0)
{
count++;
}
}
}
t->h = count;
c++;
q[c] = t;
}
int check(int n)
{
int i,j,k,i1,i3,c1=0,c2,g2=0;
int count=0;
// here it is removing the node if duplicate matrix is present
for(i=0;i<c;i++)
{
for(i3=i+1;i3<c;i3++)
{
count = 0 ;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
for(k=0;k<n;k++)
{
if(q[i]->arr[j][k]==q[i3]->arr[j][k])
{
count++;
}
}
}
if(count==9)
{
for(i1=i3;i1<c;i1++)
{
q[i1] = q[i1+1];
}
c--;
count = 0;
}
count = 0;
}
}
// here it is checking whether the goal state is finding or not
c2=0;
for(i1=0;i1<c;i1++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
for(k=0;k<n;k++)
{
if(q[i1]->arr[j][k]==a[j][k])
{
c2++;
}
}
}
if(c2==9)
{
gotit = i1;
g2 = -4;
break;
}
else{
c2=0;
}
}
return g2;
}
// Displaying path
void display(int n)
{
int i,j,k;
for(i=0;i<r;i++)
{
printf("\n");
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
for(k=0;k<n;k++)
{
printf("%d\t",q[i]->arr[j][k]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}


No comments:
Post a Comment